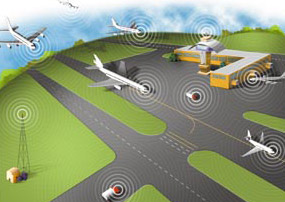
 ADS-B system is a hardware equipment installed onboard aircraft and it transmits automatically the location (latitude, longitude) of the aircraft and its movement data (speed, heading, altitude) via a digital data link (1090 MHz). These transmissions are received and can be used by other aircraft and traffic control centers to display the aircraft’s position its movement without the need for radar.
ADS-B system is a hardware equipment installed onboard aircraft and it transmits automatically the location (latitude, longitude) of the aircraft and its movement data (speed, heading, altitude) via a digital data link (1090 MHz). These transmissions are received and can be used by other aircraft and traffic control centers to display the aircraft’s position its movement without the need for radar.
ADS-B system determines the position of the aircraft using GPS. The transmitter broadcasts that position, heading and speed at regular intervals. Transmitted packets also include the aircraft’s identity, altitude, speed and other data. ADS-B ground stations receive the broadcast data and relay the information to air traffic control centers for precise tracking of the aircraft.
The ADS-B abbreviation means:
Automatic – Requires no pilot input or external interrogation.
Dependant – Depends on accurate position and velocity data from the aircraft’s navigation system (eg. GPS).
Surveillance – Provides aircraft position, altitude, velocity, and other surveillance data to facilities that require the information.
Broadcast – Information is continually broadcast for monitoring by appropriately equipped ground stations or aircraft.
ADS-B data is transmitted every half-second on a 1090MHz, digital data link.
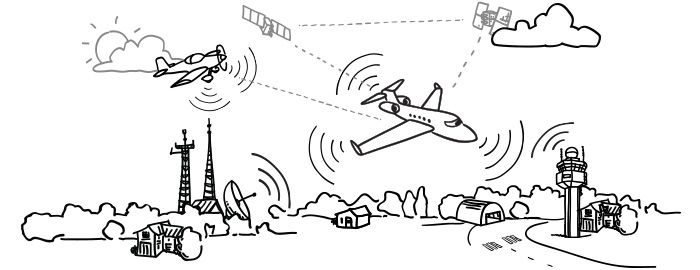
Broadcasts may include:
- Flight Identification (flight number callsign or call sign)
- ICAO 24-bit Aircraft Address (globally unique airframe code)
- Position (latitude/longitude)
- Position integrity/accuracy (GPS horizontal protection limit)
- Barometric and Geometric Altitudes
- Vertical Rate (rate of climb/descent)
- Track Angle and Ground Speed (velocity)
- Emergency indication (when emergency code selected)
- Special position identification (when IDENT selected)
The ability of a ground station to receive a signal depends on altitude, distance from the site and obstructing terrain. The maximum range of each ground station can exceed 250 nautical miles. In airspace immediately surrounding each ground station, surveillance coverage extends to near the surface.
